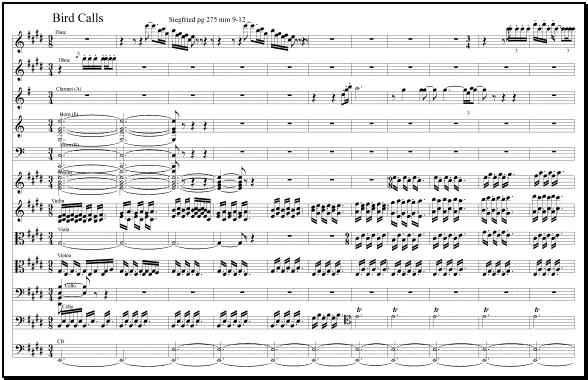
The Forest Bird in Siegfried, not unlike today’s songbirds plays a role in warning Siegfried of impending danger.
Birds have something to tell us indeed.
I recently had the opportunity to see Wagners’ Siegfried, one of the four operas that combine to create the epic “Ring des Nibelungen” or Ring Cycle. Wagner took his inspiration for The Ring Cycle from Norse mythology and an ancient German epic called the “Nibelunglied.” The Ring Cycle took more than 20 years to write, and was first performed August 16, 1876.
While I had seen Siegfried ten years ago, the experience was more significant after making The Messenger. What made it so special this time round was the role of the Forest Bird.
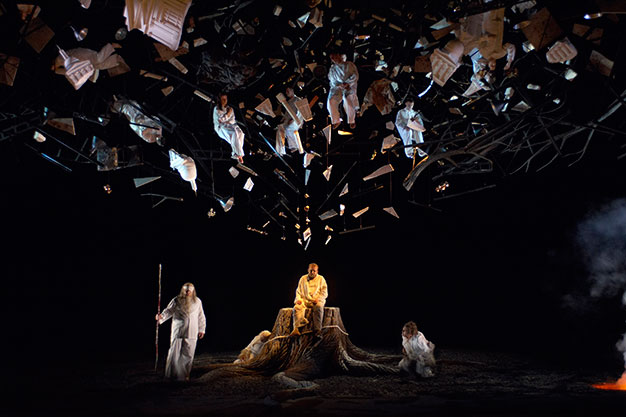
The Forest Bird is an actual character in the drama and has its own musical themes. Much of the Siegfried score occupies a somber yet beautiful low, bass tonal range with the exception of the Forest Bird — a musical motif that soars beautifully over the dramatic, emotional music.
In act 2 Siegfried takes in the tranquility of the forest around him. Here, the audience is treated to a series of birdcalls, which Wagner is said to have modeled on actual birdsong. The oboe plays the first and it is answered by a second on the flute. Next the clarinet takes up a melody. This melody on the clarinet later becomes incorporated into the soprano vocal lines of the Forest Bird character.
Humans have been inspired by birdsong for hundreds of years, and there is evidence to suggest that music pre-dates language in humans. In The Messenger we playfully re-purpose the musical motif of Wagner’s Forest Bird. Framed within a scene featuring contemporary techno artist and DJ Dominik Eulberg we created our own unique operatic moment with real forest birds singing along with the symphony. You can watch a short excerpt of the scene here.
Once we believed that birds were messengers between humans and the supernatural world. We would interpret the flight and songs of birds to foretell the future.
The Messenger opens with the voice over quoted above. Herein lies another interesting connection between The Messenger and Wagner’s Ring Cycle – as the Forest Bird does indeed have something to tell Siegfried. Like today’s songbirds, who in their very decline warn us of the environmental dangers we all face, the Forest bird warns Siegfried of danger, and by listening to the bird he is saved from a betrayal that would have cost him his life. Birds have something to tell us indeed.
Watch an except of The Messenger with Dominik Eulberg on Youtube.